Electrolyser Calculator
Calculate required electrolyser size or daily hydrogen production and instantly get recommendations of real-world electrolyser models matched to your results.
The calculations provided by HyCalc are intended for preliminary estimates and scenario exploration. While we strive for accuracy, we recommend consulting qualified engineers for final system design, safety decisions, and regulatory compliance in your specific application.
How to Use This Calculator
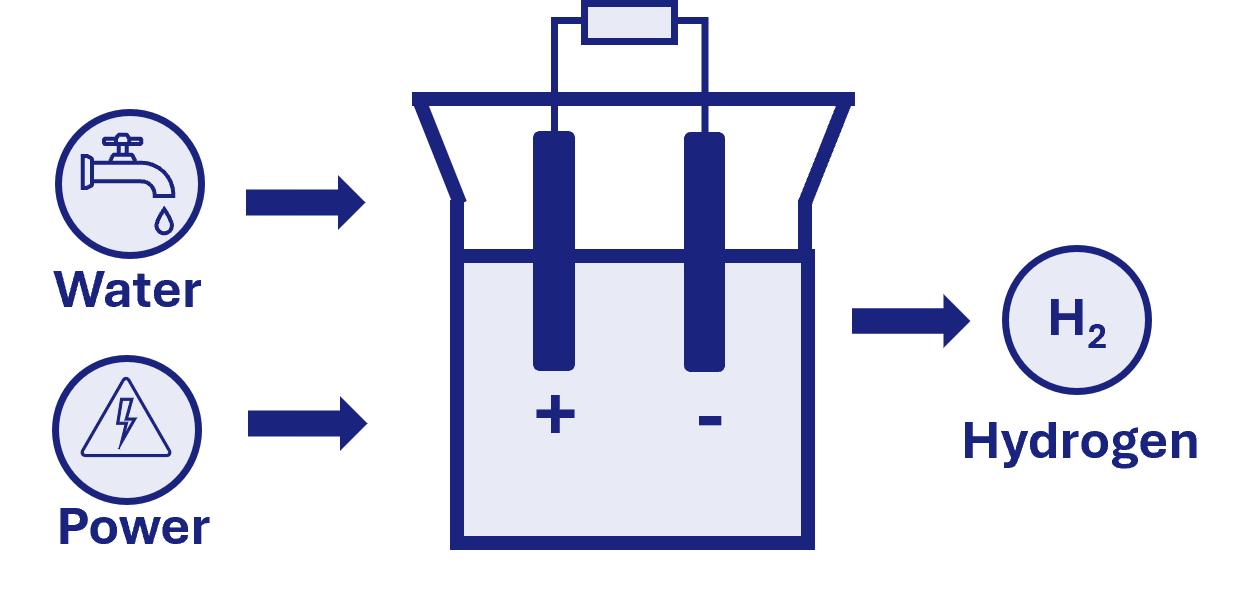
Electrolyser schematics
Understanding Operation Modes
Production Mode
- Use when: You know your electrolyser's power capacity
- Calculates: Daily hydrogen production potential
- Typical users: Plant operators, energy planners
Example: A 5MW electrolyser @ 75% efficiency and 90% load factor produces
≈ 2,054 kg H2/day
Power Mode
- Use when: You have a target hydrogen production goal
- Calculates: Required electrolyser capacity
- Typical users: Project developers, system designers
Example: To produce 10,000 kg H2/day @ 80% efficiency and 85% load factor needs
≈ 24.2 MW capacity
Input Explanations
- Power/Hydrogen Production:
- Base parameter depending on selected operation mode
- Efficiency (%):
- System efficiency including power conversion losses (PEM: 70-85%, Alkaline: 60-75%)
- Load Factor (%):
- Annualized utilization rate (Grid-connected: 30-60%, Hybrid systems: 70-90%)
Key Considerations
- All values assume standard temperature (25°C) and pressure (1 atm)
- Assumes water density of 998 kg/m³
- Energy calculations based on higher heating value (HHV) of 39.44 kWh/kg
Understanding Electrolysers
What is Water Electrolysis?
Water electrolysis is an electrochemical process that splits water (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) using electrical energy. When an electric current passes through water, it causes the water molecules to decompose at the electrodes:
- Anode: Produces oxygen gas (O₂)
- Cathode: Produces hydrogen gas (H₂)
This process is the foundation of green hydrogen production when powered by renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
Why Use This Calculator?
Accurate electrolyser sizing is crucial for project planning and cost estimation. This calculator helps you:
- Size systems correctly: Determine the right electrolyser capacity for your hydrogen production needs
- Estimate costs: Calculate energy and water requirements for budget planning
- Compare options: Evaluate different electrolyser models and configurations
- Optimize design: Balance efficiency, load factors, and operational requirements
- Plan infrastructure: Understand power and water needs for facility design
Types of Electrolysers
There are several electrolyser technologies, each with distinct characteristics:
- Alkaline (AWE): Mature technology, cost-effective for large-scale applications. Efficiency: 60-75%. Best for continuous, industrial operations.
- PEM (Proton Exchange Membrane): Compact, fast response, high purity. Efficiency: 70-85%. Ideal for variable renewable energy sources.
- SOEC (Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell): High-temperature operation, superior efficiency. Efficiency: 80-95%. Excellent for industrial heat integration.
- AEM (Anion Exchange Membrane): Emerging technology combining benefits of PEM and Alkaline. Efficiency: 70-80%. Good for modular applications.
Factors Affecting Production & Consumption
Several factors influence hydrogen production and electricity consumption:
- System Efficiency: Higher efficiency means less electricity per kg of H₂ produced. Typical range: 60-95% depending on technology.
- Load Factor: Percentage of time the system operates at full capacity. Grid-connected: 30-60%, Hybrid systems: 70-90%.
- Operating Temperature: Higher temperatures can improve efficiency but require more energy to maintain.
- Water Quality: Pure water is essential. Impurities can reduce efficiency and damage the system.
- System Age & Maintenance: Well-maintained systems maintain efficiency; degradation reduces output over time.
- Stack Configuration: Series vs. parallel arrangements affect voltage, current, and overall performance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When sizing and operating electrolysers, avoid these common pitfalls:
- Underestimating load factor: Using 100% load factor when actual operation is lower leads to oversized systems and wasted capital.
- Ignoring efficiency degradation: Systems lose efficiency over time. Plan for 2-5% degradation over the system lifetime.
- Neglecting auxiliary power: Balance of plant (BOP) systems consume 5-15% additional power not included in stack efficiency.
- Overlooking water treatment: Poor water quality reduces efficiency and increases maintenance costs significantly.
- Mismatched power supply: Ensure your power source can provide stable voltage and current matching electrolyser requirements.
- Inadequate cooling: Electrolysers generate heat; insufficient cooling reduces efficiency and can damage components.
- Wrong technology choice: PEM is better for variable loads; Alkaline for steady-state operations. Choose based on application.